India’s M2M cellular market is accelerating, with active connections projected to reach 200 million by the end of 2026 as per Techarc estimates, doubling in a year. It estimates that in 2026 India will add 100 mn M2M cellular connections equalling to the cumulative number of connections by the end of 2025. Growth is being propelled by large government programs, rapid operator expansion—especially Airtel and Jio—and a shift from pilots to nationwide rollouts in smart metering, connected vehicles, and logistics.
As of mid-2024, there were about 52.5 million cellular M2M connections; by 2025, the industry total had risen toward mid‐70 million, underscoring strong momentum. Penetration is deepening, roughly 8 M2M connections per 100 mobile subscribers, reflecting the rising share of IoT in India’s mobile ecosystem.
Key Takeaways
- For every 100 mobile subscribers in India, there are approximately 8 M2M cellular connections.
- 2025 pacing up: 35.48m subscribers added in 2025 (Jan-Sept 2025) alone, which is an increase of 60%
- Policy payoffs: Large government programs are in full deployment, especially smart metering and automotive telematics (e.g., connected cars, fleet, FASTag/e‑Call), underpinning smart city and utility efficiency gains.
- India’s IoT at scale: M2M has moved from pilots to large, multi‑industry rollouts, becoming core connectivity infrastructure.
- Airtel drives the expansion: Airtel’s base jumped from 28.44M to 56.33M (+27.89M), lifting share from 52.06% to 59.56%; it contributed the majority of 2025 adds.
- Jio’s steady acceleration: Jio grew from 8.35M to 16.88M (+8.53m), nudging share up from 15.29% to 17.84% while maintaining consistent monthly net adds through 2025.
Overall Cellular M2M
The base period is April, as TRAI started reporting that month. We observed a total subscriber base growth of 2.72 M, increasing from 54.64 M in April to 56.12 M in September 2025, which represents a 5.24% rise.
Comparing the numbers year-over-year, from September 2024 to September 2025, the number of M2M cellular mobile connections increased from 54.64 M to 94.57 M, reflecting an increase of 39.93 M (73.08%). Additionally, the results show that for every 100 mobile subscribers, there are 8 M2M cellular connections. As of September, the total wireless subscriber base stood at 1182 million.
Operator Distribution
April-Sept 2024
- Jio’s Early Surge: Jio accounted for nearly all of the new connections, adding 2.43 million subscribers from 5.92M to 8.35M. This allowed it to achieve a dramatic market share gain of +3.88 percent, growing its share from 11.41% to 15.29%. This was the most significant move of any operator in this phase.
- Airtel’s Initial Retreat: Despite its overall market dominance, Airtel showed minimal absolute growth (+0.05 M) 28.39 M to 28.44 M and, consequently, saw the largest market share drop of -3.63%. This suggests the early wave of M2M connections, after the TRAI started reporting.
- Vodafone and BSNL: Both operators showed only marginal absolute growth (Vodafone +0.11 M, BSNL +0.13 M) and lost minor market share percentage, indicating they were non-factors in this initial phase of reporting.
Sept 2024 – Sept 2025 – Growth and Market Rebalancing
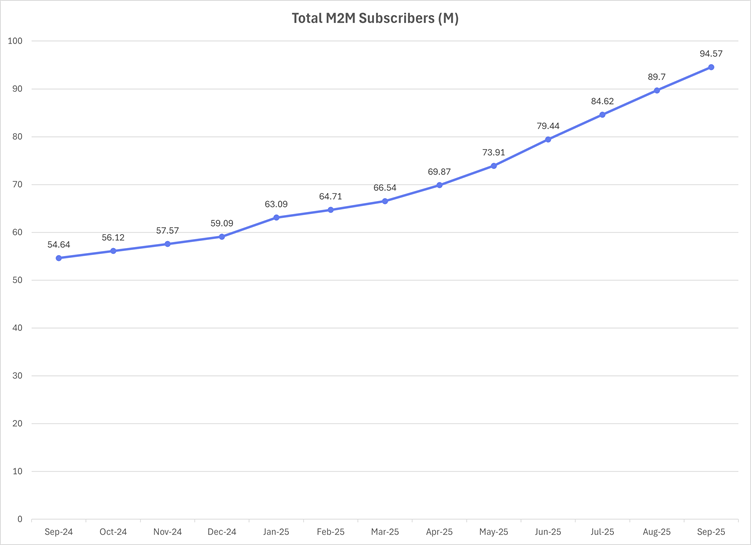
This 12-month period demonstrates the market’s full-throttle expansion, adding an immense 39.93 million new subscribers from 54.64 million (Sep 2024) to 94.57 million (Sep 2025) a growth of 73.08% over the starting base. This phase established a strong market consolidation.
Market Share
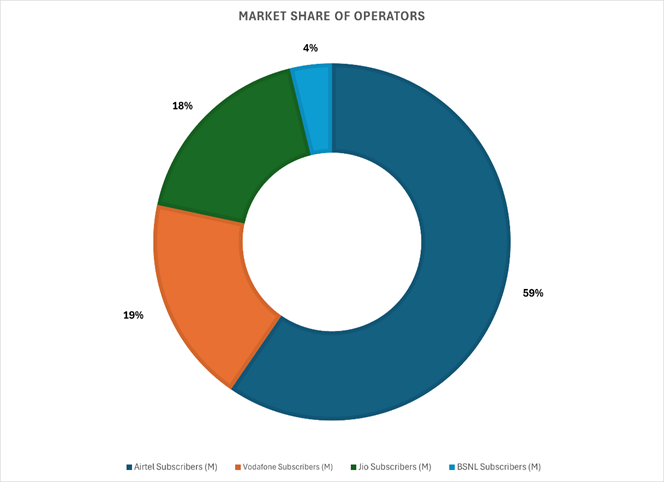
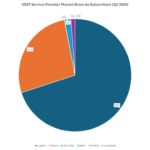
As of September 2025, the cellular M2M market share in India is predominantly held by Airtel at 59.56%, followed by Vodafone at 18.79%, Jio at 17.84%, and BSNL at 3.81%
- Airtel’s Reasserted Dominance: Airtel completely recovered its momentum, leading the market’s absolute growth by adding a massive 27.89 million subscribers from 28.44m to 56.33m. This accounts for over 70% of the total market growth during this period. As a result, Airtel recorded the largest market share gain of +7.50%, successfully solidifying its position and ending the period with a dominant share of 59.56%.
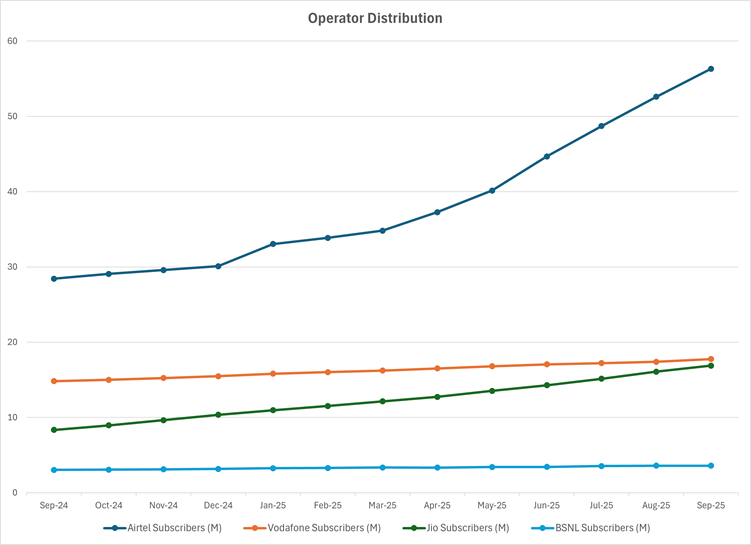
- Jio’s Continued, but Slower, Growth: Jio maintained its growth trajectory by adding 8.53 million new subscribers from 8.35m to 16.88m. While substantial, this was significantly less than Airtel’s expansion, leading to a smaller, but healthy, market share gain of +2.55%. Jio cemented its position as the clear second-largest player in the M2M sector.
- Vodafone’s Sharp Decline: Vodafone faced the most severe challenge, only managing to add 2.94 million subscribers over 12 months from 14.82m to 17.76m, which was insufficient to keep pace with the exponential market growth. This resulted in a substantial market share erosion of -8.33%, dropping its share from 27.12% to 18.79%. This trend highlights a fundamental inability to capture the new demand.
- BSNL’s Stagnation: BSNL showed the weakest performance, adding only 0.57 million subscribers from 3.03m to 3.60m and losing -1.73% of market share. This indicates a minimal, shrinking role in the M2M ecosystem compared to the top three.
What is M2M, and when did it begin in India
Machine-to-Machine (M2M) Communication is the direct, automated exchange of information between devices (machines) over wired or wireless networks without human intervention.
It is the foundational technology for the Internet of Things (IoT), allowing sensors and devices to capture events and transmit data to an application for analysis (telemetry).
M2M SIM Cards
An M2M SIM card is a specialized, industrial-grade Subscriber Identity Module designed for this autonomous machine communication.
M2M technology is critical for:
- Smart Metering: Automated utility reading (electricity, gas).
- Telematics: Vehicle tracking and remote diagnostics.
- Healthcare: Remote patient monitoring.
- Logistics: Real-time asset and supply chain tracking.
Early Adoption (2011–2013): The first commercial M2M applications emerged, mainly driven by vehicle telematics and smart metering.
Regulatory Framework (2012–2015): The National Telecom Policy (NTP)-2012 recognized M2M, and the government published the National Telecom M2M Roadmap (May 2015) to formalize standards and policy.
Formalization & Scale-up (2016 onwards): The government established the M2M ecosystem by issuing initial 3-digit M2M identifiers (2016), in 2018 Department of Telecom (DoT) ordered telcos to implement a 13-digit scheme for SIM-based M2M connections.
Future Outlook
Techarc’s forecast indicates an accelerated adoption trajectory for cellular M2M connections in India. The M2M subscriber base is predicted to cross 100 million by the end of 2025. This rapid momentum is expected to result in the base crossing 200 million by the end of December 2026.
Key Growth Drivers
The primary catalysts for this robust growth are the large-scale deployment of M2M SIMs in key sectors:
- Smart Metering: Large-scale government projects for replacing conventional meters with smart, connected meters form the backbone of M2M SIM volume.
- Connected Vehicles (Automotive/Telematics): The mandatory fitment of tracking devices, increasing consumer demand for in-car connectivity, and the rise of fleet management solutions are driving M2M usage at large.
Competitive Dynamics: Jio vs. Vodafone
The competitive positioning in the M2M segment is highly dynamic, with a potential change in ranking anticipated in the near term. Reliance Jio is projected to overtake Vodafone in the October-to-December quarter to become the second-leading M2M cellular provider in India.
Rationale for the Shift:
Narrow Gap: The difference in the M2M subscriber base between Jio and Vodafone is currently very thin. (As of September 2025, TRAI data, Airtel leads significantly, followed by Vodafone, with Jio in a close third position. Vodafone’s base is 18.79% and Jio’s is 17.84% of the total M2M connections, showing a gap of less than 1 percentage point.
Growth Trajectory: Jio is consistently adding a high number of new M2M connections, driven by its focus on enterprise and utility deployments. Conversely, Vodafone’s M2M subscriber growth rate has been near-stable or modest, making it vulnerable to being surpassed by Jio’s aggressive expansion.