Smartphone connectivity continues to be a key factor affecting overall user experience. A variety of challenges contribute to the lack of seamless integration across different network types—both cellular and Wi-Fi. Multiple stakeholders, including regulators, operators, network management service providers, and handset manufacturers, are making both collaborative and independent efforts to address and improve smartphone connectivity.
TechMark: As part of our TechMark offering, we developed a comprehensive benchmarking framework and defined the methodology for conducting a comparative analysis.
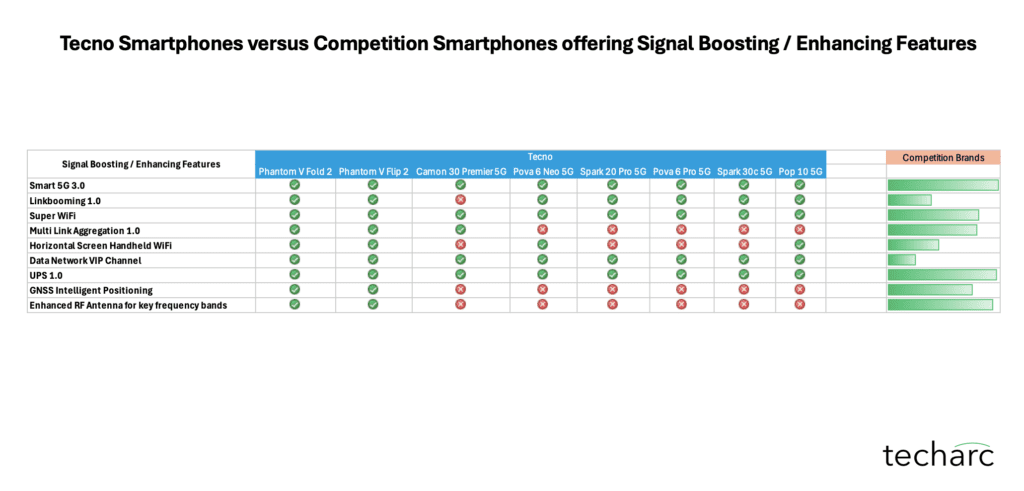
As part of the benchmarking process, we compared eight TECNO smartphones equipped with advanced signal boosting technologies against more than 95 competing smartphone models across a wide range of price segments. This extensive comparison spanned devices from 15 major brands, including both global giants and regional players.
The following outlines the process and structure of the benchmarking exercise.
- TECNO provided a list of smartphone models along with the specific signal boosting and enhancement technologies integrated into each device. The brand also demonstrated how these technologies improve signal quality across both cellular and Wi-Fi networks.
- A competition matrix was created to map each TECNO smartphone against comparable models from competing brands.
- A thorough review of specifications and features across these devices was conducted. For this, we relied on our extensive internal tracker and supplemented it with additional secondary research, including detailed scans of product sheets and specification lists for both TECNO and its competitors.
- The competing brands included in the benchmarking exercise were: Apple, Google, HMD, Infinix, iQoo, iTel, Nothing, OnePlus, Oppo, Poco, Realme, Redmi, Samsung, Vivo, and Xiaomi (listed alphabetically).
- For each signal boosting technology found in TECNO smartphones, a comparative chart was prepared to assess the presence or absence of similar technologies in competing devices.
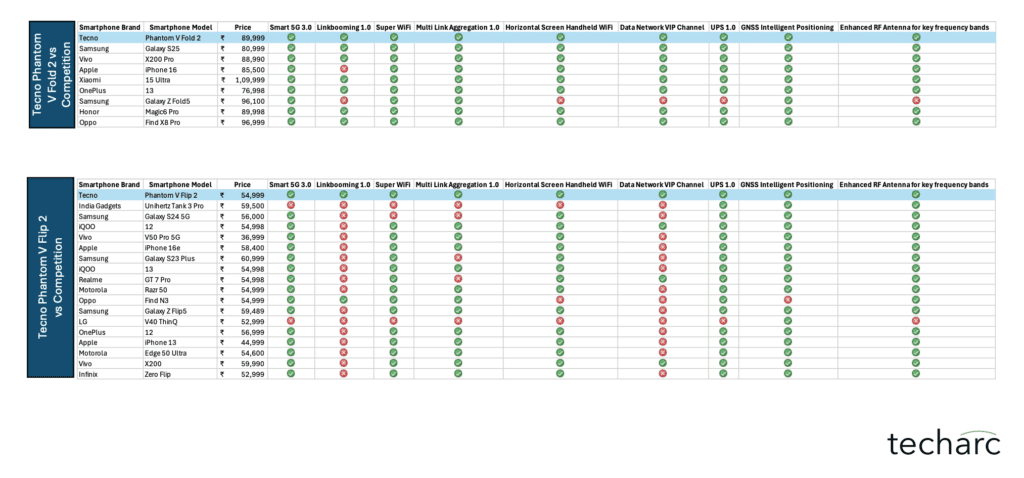
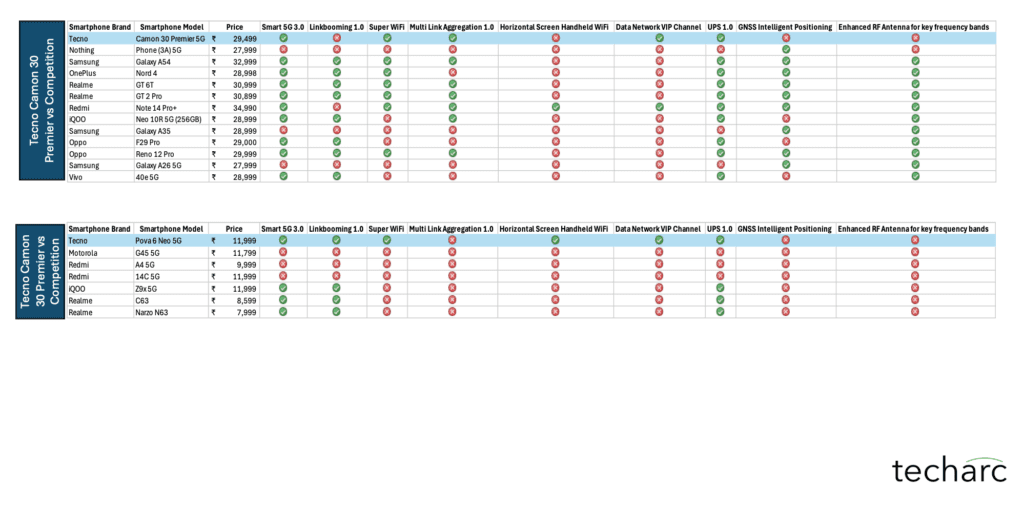
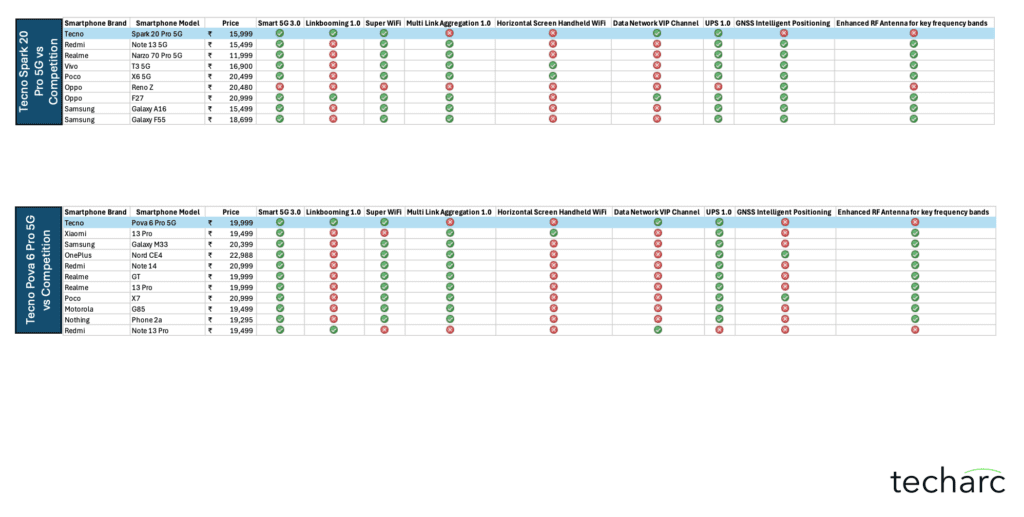
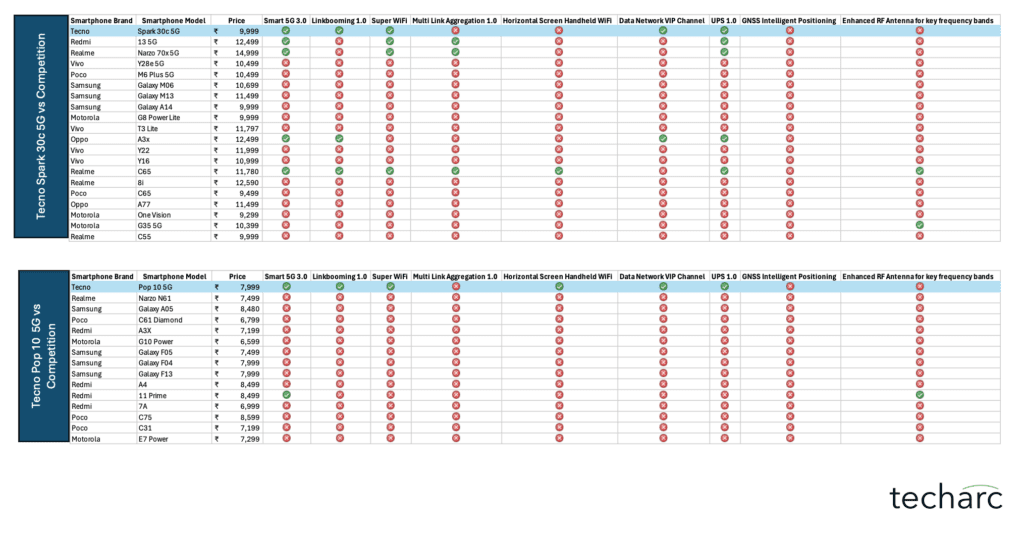
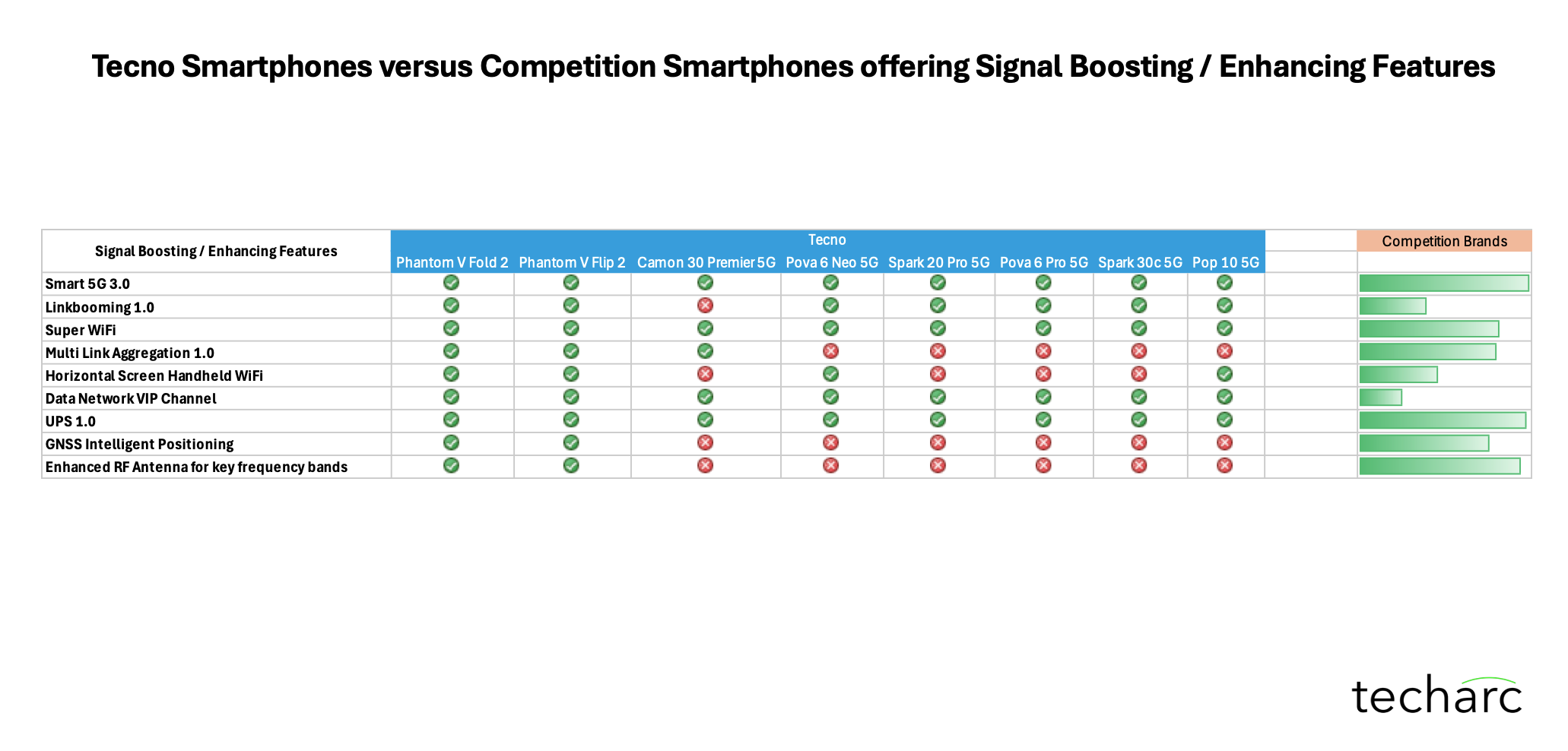
With the exception of select flagship-tier smartphones from these brands, such technologies were largely absent in their respective portfolios. Our research also verified that these technologies were not simply rebranded or re-labeled features under different names.Based on this analysis, Techarc that TECNO’s entire smartphone portfolio features one or more of these signal boosting technologies—setting it apart from competitors, especially in the mid-range and entry-level segments.
Limitations: The benchmarking exercise focuses solely on the presence or absence of the listed signal boosting technologies across smartphone models. It does not assess the actual performance or real-world effectiveness of these features. The true impact of these technologies may vary depending on several external factors, such as network quality, environmental conditions, and supporting equipment like Wi-Fi routers or network infrastructure.
Our analysis specifically focused on TECNO’s proprietary network-boosting technologies, which include:
Smart 5G 3.0: TECNO’s Smart 5G 3.0 dynamically switches between 5G and 4G based on real-time network conditions, maintaining high data speeds during bandwidth-intensive tasks such as streaming and downloading large files.
Linkbooming 1.0: This feature simultaneously leverages Wi-Fi and cellular data, significantly enhancing download speeds and reducing latency, ensuring a smoother online experience.
Multi-Link Aggregation 1.0: This technology enables devices to simultaneously aggregate multiple network links—such as combining multiple cellular bands or leveraging multiple Wi-Fi connections concurrently. This ensures greater connectivity stability, consistently higher throughput, and minimized network interruptions.
Super WiFi: Using this, smartphones intelligently optimises Wi-Fi connectivity by dynamically adjusting frequency bands (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz), maximising throughput, enhancing stability, and minimising battery drain.
UPS 1.0 (Ultra Power Signal): This technology aims to deliver measurable improvements in cellular reception strength, stability, and data throughput, even in regions with weak signal coverage. UPS 1.0 directly translates into fewer dropped calls, reduced buffering during streaming, and more reliable internet access.
GNSS Intelligent Positioning: This integrates multiple global satellite systems (GPS, Galileo, GLONASS, BeiDou, and QZSS) alongside advanced sensor fusion technologies to enhance location accuracy, especially beneficial in challenging urban environments.
Enhanced RF Antenna Design: TECNO smartphones employ a proprietary enhanced RF antenna design, fine-tuned specifically for critical cellular bands (4G LTE and sub-6GHz 5G). Through precise antenna placement, advanced tuning circuits, and robust frame integration, these smartphones deliver consistently superior cellular signal strength across diverse usage scenarios. Similar antenna optimizations, such as Samsung’s adaptive antenna or Oppo’s 360° antenna designs, are exclusively found in their highest-tier flagship devices.
Horizontal Screen Handheld WiFi: Special antenna configurations maintain stable Wi-Fi connections when the phone is held horizontally, crucial for gaming and video streaming.
Data Network VIP Channel: TECNO’s Data Network VIP Channel prioritises network traffic for foreground applications to reduce latency and improve app responsiveness.
Conclusion: Upon comprehensive evaluation, TechMark benchmarking confirmed that above mentioned advanced connectivity features are indeed offered by leading brands—but almost universally limited to their highest-tier flagship models.
For instance, Apple and Samsung integrate intelligent 5G toggling and adaptive Wi-Fi antennas exclusively in flagship series like the iPhone Pro/Pro Max and Galaxy S Ultra series. Their entry-level and mid-range models, such as iPhone SE and Samsung’s Galaxy A-series, remain devoid of these advanced capabilities.
Similarly, premium iPhone models such as iPhone 16 and iPhone 15 Pro support advanced connectivity features like enhanced RF antenna designs. However, their more affordable models, including the latest iPhone 16E, do not include dual-network aggregation (simultaneous use of Wi-Fi and cellular data). This omission means users of these entry-level iPhones cannot experience the enhanced download speeds, lower latency, and improved network stability provided by parallel network acceleration.
Google’s budget-focused Pixel 7a and other affordable Pixel A-series devices similarly prioritize affordability and camera performance but notably lack dual-network acceleration capabilities. Google’s premium Pixel 8 Pro supports enhanced network management features, but these critical connectivity enhancements are absent in their entry-level offerings, resulting in noticeable differences in connectivity performance, especially in congested network conditions.
Oppo and Vivo likewise reserve dual-network aggregation and advanced RF antenna configurations for their higher-end lineups, typically flagship Reno, Find X, or Vivo X series, leaving budget and mid-tier options far behind in connectivity optimisations.










TECNO Ranked #1 in Smartphone Connectivity – Best Signal, Choose TECNO - Press Release India
April 15, 2025[…] in its cap—recognized as a front-runner in smartphone signal performance, as per the latest TechMark report by TechArc. The comprehensive benchmarking study spotlighted TECNO’s power-packed signal-boosting […]
TECNO Ranked #1 in Smartphone Connectivity - Best Signal, Choose TECNO - World News Network - Latest World News Update
April 15, 2025[…] in its cap–recognized as a front-runner in smartphone signal performance, as per the latest TechMark report by TechArc. The comprehensive benchmarking study spotlighted TECNO’s power-packed signal-boosting […]
TECNO Ranked #1 in Smartphone Connectivity - Best Signal, Choose TECNO - World News Network - Latest World News Update
April 15, 2025[…] in its cap–recognized as a front-runner in smartphone signal performance, as per the latest TechMark report by TechArc. The comprehensive benchmarking study spotlighted TECNO’s power-packed signal-boosting […]